Cerakote® is a ceramic polymer based proprietary formulation that offers industry-leading durability, hardness, scratch resistance, corrosion resistance, flexibility, heat, and chemical resistance. Cerakote® can be applied to most substrates including metals, plastics, polymers, composites, hydrographics and PVD.
Cerakote® is a Polymer-Ceramic Composite coating that can be applied to metals, plastics, polymers, and wood. The unique formulation used for Cerakote® ceramic coating enhances a number of physical performance properties including abrasion/wear resistance, corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, impact strength, and hardness. Each of these properties is rigorously tested to guarantee that Cerakote® products remain at the forefront of the ceramic coatings market. Cerakote® ceramic coatings utilize state-of-the-art technology to out-perform any competitive coating in both laboratory settings and real-world applications.
For the ultimate in firearm protection and to get a look that sets you apart, choose our Cerakote® line of coatings.
Recommended uses:
- Firearms
- Military Applications
- Barrels
- Accessories
- Knives / Blades
- Corrosive Environments
- Solvent Environments
- Abrasive Environments
- Industrial Applications
- Decorative Finishes
*Taber abrasion testing performed by Anachem Laboratories, Inc. El Segundo CA
Taber abrasion testing was performed to compare the wear resistance of Cerakote® H-146 Graphite Black to the products two competitors. This testing was performed by an independent testing facility and according to ASTM Standard D4060-01. Each coating was applied to a set of stainless steel panels according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A CS-17 taber abrasion wheel with a 1000 g weight was used for the abrasion testing.
Measurements to determine the mass of coating lost were taken at intervals of 500, 1000, 5000, and 8000 cycles. The results of this study are shown in table 1 and are further illustrated in figure 1. As shown, the coating manufactured by competitor 1 (C1) failed at 500 cycles, competitor 2 (C2) failed at 1000 cycles, and Cerakote® H-146 failed at 8000 cycles. For this test, failure was defined as the point at which the metal substrate was exposed. The weight loss was used to determine the wear index and wear cycles per mil. The wear index establishes the mass rate at which the coating is lost, and the rate of thickness loss is shown by the wear cycles per mil. The mass of coatings C1 and C2 were worn away 6.4 and 1.6 times more quickly than Cerakote® H-146, respectively. Cerakote® H-146 also endured 5212 cycles per mil whereas C1 and C2 endured 597 and 697 wear cycles per mil, respectively. Figure 1 graphically illustrates the wear cycles required to remove 1 mil of coating from each panel. These results confirm that Cerakote® H-146 is significantly more wear resistant than either C1 or C2.
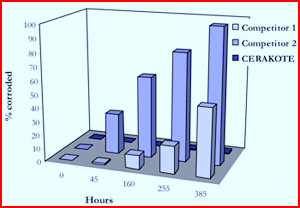
Each coating was applied to a set of steel panels and in accordance to the manufacturers’ directions. Next, the panels were placed in a chamber and continuously exposed to a 5% salt water solution. The panels were checked for corrosion at specific intervals of 45, 160, 255, and 385 hours. The degree of corrosion for each panel was estimated based on the amount of affected area. The results of the salt spray test are shown in figure 2. At the maximum time, C1 was 50% corroded, C2 was 100% corroded and Cerakote® H-146 was 2% corroded. Coating C2 exhibited a high degree of undercutting and C1 was moderately undercut whereas Cerakote® H-146 did not display any signs of undercutting. The Cerakote® H-146 coating was significantly more corrosion resistant than either C1 or C2.
Figure 2. Corrosion as a function of time for three coatings (C1, C2, and Cerakote® H-146) tested according to ASTM Standard B117-03 in a 5% salt solution.
The ability of each coating to resist chemical attack was tested by dipping coated panels into a series of solvents to which the coating may be exposed during use or extreme conditions. The panels were placed in the solution and allowed to sit for 24 hours. The results of this test are shown in table 2. Each coating performed in a similar fashion for the majority of the solvents. Cerakote® H-146 performed noticeably better in the 5% HCl solution and in the ammonia whereas C1 and C2 showed degradation in these solvents.
Table 2. Chemical resistance of three coatings (C1, C2, and Cerakote® H-146) to 15 different solvents*.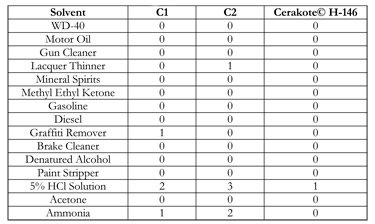
* 0=no noticeable change, 1= slight corrosion or color change, 2=noticeable corrosion or color change, 4= significant corrosion or color change, 5=complete corrosion of coating.
Additional analyses were performed to compare the physical properties of each coating. These results are displayed in table 3. Coating C2 is the weakest coating, with low hardness, low impact strength and a higher susceptibility to scratching. Coatings C1 and Cerakote® H-146 have comparable hardness and impact strength. From this analysis, Cerakote® H-146 is clearly a competitive firearm coating.
Table 3. Comparison of the physical properties of three coatings (C1, C2, and Cerakote® H-146).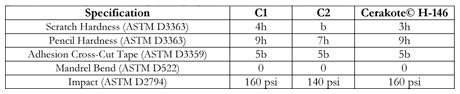
Cerakote® gun coatings come in a variety of colors and have a sleek satin finish. We have recently added custom finishes such as digital camouflage which can be special ordered.




